« Reference and Pass By reference
Understand Reference and Pass By reference
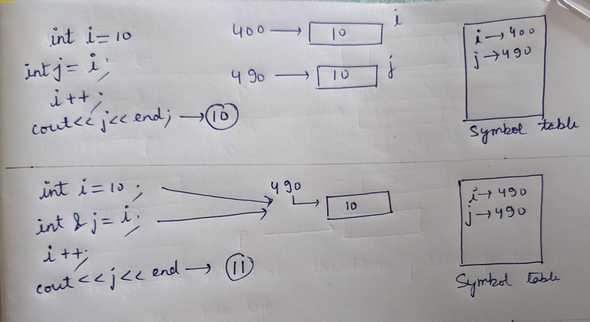
Reference variable
1int i = 10;2int &j = i; // reference variable.34i++;5cout << "j: " << j << endl;6j++;7cout << "i: " << i << endl;
We don't create new memory location for reference variable. j is pointing to the same location as i. In Symbol table they are pointing to the same location.
1int i = 10;2int &j = i;3int k = 100;4j = k;5cout << "j: " << j << endl;6cout << "i: " << i << endl;
Here both i and j will change as both point to the same location so i and j both will change.
1int a;2a = 10;3// int &b; //error: .4// b = a;
a is fine here as this just means create a memory space for a and it has a garbage value and then in next step we place 10 into it. b is not fine here, it will throw error: declaration of reference variable 'b' requires an initializer . As this is a reference variable so we need it to point to some existing location. So we need to mention this at the very first step.
Pass by reference
1void increment(int &n)2{3 n++;4}
So there is a way functions can share their local variables if they pass it as reference variables.
1// bad practice2int &f(int n)3{4 int a = n;5 return a;6}
This is bad practice. Reference to stack memory associated with local variable a is returned. a has scope bound to this function. Later the function invocation system can reclaim this memory for something else. So this is dangerous. If we are doing this then we should be aware of what are we doing here.
1int *f2(int n)2{3 int a = n;4 return &a;5}
This is bad practice. Address of stack memory associated with local variable a returned. If we are doing this then we should be aware of what are we doing here.
a is local memory associated with the function. Its scope bound to this function.
In short we shouldn't return reference or pointer to a local variable from a function. This is a bad practice as that memory doesn't belong to us. If we are doing this then we should be aware of what are we doing here.
Sending via reference has a benefit also that we don't have to create new memory location and copy data into it.
Final code
1#include <iostream>2#include <iomanip>3#include <algorithm>4#include <string>5#include <cstring>6#include <vector>7#include <cmath>8#include <map>9#include <climits>10// climits for INT_MIN11#include <unordered_map>12using namespace std;1314// reference variables15void increment(int &n)16{17 n++;18}1920// bad practice21int &f(int n)22{23 int a = n;24 return a;25}2627// bad practice28int *f2(int n)29{30 int a = n;31 return &a;32}3334int main()35{36 int i = 10;37 int &j = i; // reference variable.3839 i++;40 cout << "j: " << j << endl;41 j++;42 cout << "i: " << i << endl;4344 int k = 100;45 j = k;46 cout << "j: " << j << endl;47 cout << "i: " << i << endl;4849 int a;50 a = 10;51 // int &b; //error: declaration of reference variable 'b' requires an initializer.5253 // b = a;5455 increment(i);56 cout << "j: " << j << endl;57 cout << "i: " << i << endl;5859 int &c = f(i);60 int *d = f2(i);6162 return 0;63}