« Pointers And Arrays
Understand Pointers And Arrays
Understand similarities between pointers and arrays
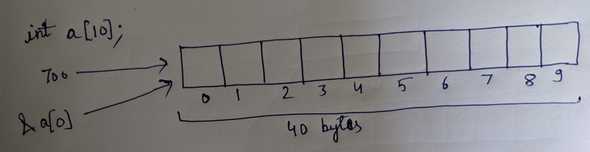
1int arr[10];2cout << "arr: " << arr << endl;3cout << "&arr[0]: " << &arr[0] << endl;
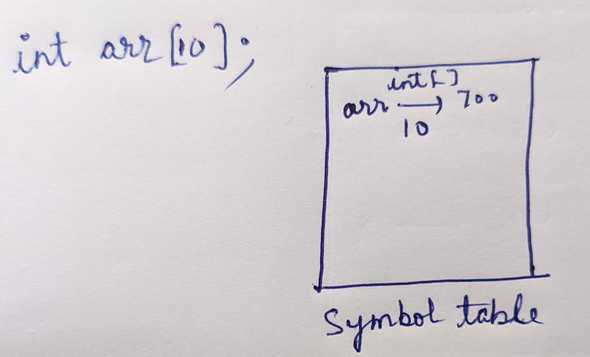
This will create 40 bytes storage for array. a is basically name for this 40 bytes. In symbol table there will be a entry of a = starting address of this 40 bytes which is same as address of arr[0] i.e. &arr[0]. So arr can be treated almost exactly like a pointer.
1cout << "*arr: " << (*arr) << endl;2arr[0] = 5;3arr[1] = 10;4cout << "*arr: " << (*arr) << endl;5cout << "*(arr+1): " << (*(arr + 1)) << endl;6cout << "1[arr]: " << 1 [arr] << endl;
So, arr[i] and *(arr+i) are same. i[arr] and *(i+arr) are also same. So arr[i] and *(arr+i) and i[arr] are all same
Understand dissimilarities between pointers and arrays
1cout << "sizeof(arr): " << sizeof(arr) << endl;2cout << "arr: " << arr << endl;3cout << "&arr: " << &arr << endl;
Although arr can be treated as pointer but there are couple of differences. sizeof(arr) = 40 as in symbol table its mentioned that it is a array of size 10. But sizeof(pointer) = 8. All these difference is because, for pointers another 8 byte memory is created for it and saved to the symbol table, but for arrays no extra storage is created. In symbol table arr = address of array is stored.
arr and &arr prints same but pointer and &pointers prints different. Reason: for storing pointers another storage is created but not for arrays(arrays are just entered in the symbol table).
1//arr = arr + 3; //this will give error
Array can not be reassigned. Something entered in a symbol table cannot be changed.
1int *ptr = arr;2cout << "ptr " << ptr << endl;
You can't do array = pointer but you can do pointer = array
Final Code
1#include <iostream>2#include <iomanip>3#include <algorithm>4#include <string>5#include <cstring>6#include <vector>7#include <cmath>8#include <map>9#include <climits>10// climits for INT_MIN11#include <unordered_map>12using namespace std;13int main()14{15 int arr[10];16 /*17 This will create 40 bytes storage for array18 _________________________________________________________19 |________________________________________________________|2021 a is basically name for this 40 bytes22 in symbol table there will be a entry of a = starting address of this 40 bytes which is same as address of arr[0] i.e. &arr[0]23 */2425 cout << "arr: " << arr << endl;26 cout << "&arr[0]: " << &arr[0] << endl;27 // So arr can be treated almost exactly like pointer2829 cout << "*arr: " << (*arr) << endl;30 arr[0] = 5;31 arr[1] = 10;32 cout << "*arr: " << (*arr) << endl;33 cout << "*(arr+1): " << (*(arr + 1)) << endl;3435 cout << "1[arr]: " << 1 [arr] << endl;3637 cout << "sizeof(arr): " << sizeof(arr) << endl;38 cout << "arr: " << arr << endl;39 cout << "&arr: " << &arr << endl;4041 // arr = arr + 3; array can not be reassigned.4243 int *ptr = arr;44 cout << "ptr " << ptr << endl;45 // You can't do array = pointer but you can do pointer = array4647 return 0;48}