« Type Conversions
1char ch = 'a';2int i = ch;3//ch = i; //error
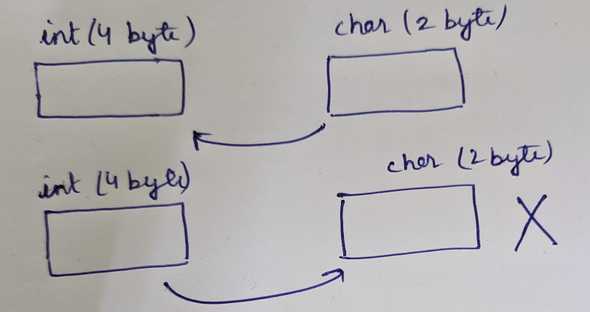
int i = ch is implicit typecasting.
ch = i Error: incompatible types: possible lossy conversion from int to char.
1// ch = ch + 1; //error
ch + 1 here value will be a integer as 1 is integer and ch is char so result will be of bigger type which is int. So we are trying to store a int in char so it will be error as int being of bigger size can't be implicitly stored in char.
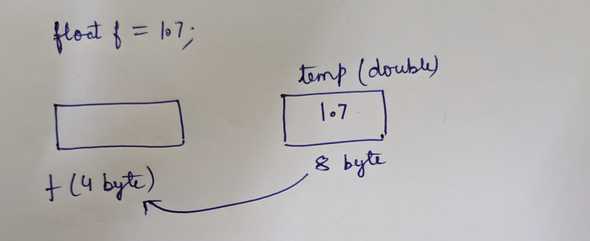
1// float f = 1.7; //error2float f = (float) 1.7;
All decimal numbers we write are by default double. Error: incompatible types: possible lossy conversion from double to float
1short s = 17;2int k = s;3//s = k; //error
Error: incompatible types: possible lossy conversion from int to short
1System.out.println(4 + 4);2System.out.println(4 + 4.5);3System.out.println(4.3 + 4.5);
- If you add
intandintanswer will be aint. - If you add
intanddoubleanswer will be adouble. - If you add
doubleanddoubleanswer will be adouble. - So in arithmetic operations datatype of the bigger size will be the resultant datatype.